Хamarin vs React Native in 2022: Which one is better?
Хamarin vs React Native in 2022: Perfect match for your project.
April 30, 2022
10 min read
We could judge a given framework’s efficiency by its popularity (measured in total hours spent on the development), so here it is right off the bat: which one is better: Xamarin vs React Native?

Source: Statista.
React Native seems to be far ahead. But let us not be biased like that and dig deeper though.
What is React Native?
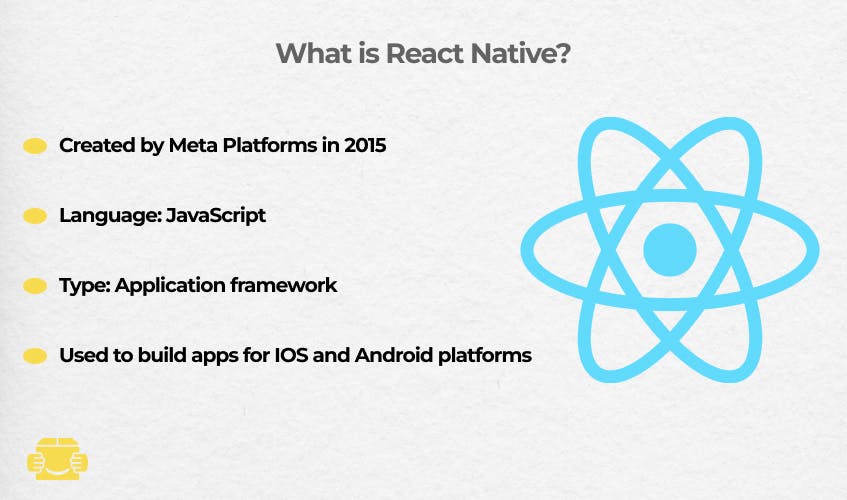
React Native is one of cross-platform mobile development frameworks (and also web) that is based on JavaScript: React library, to be more specific. It has retained most of its popularity over 2020-2021, and remains one of the most actively developed open-source projects.
The Meta team (formerly Facebook) professionally leads the framework development.
JavaScript is one of the two languages that are interpreted by browsers, the other one being WebAssembly. That is if we don’t consider HTML and CSS as programming languages. The variety of JS application niches ensures high demand for it and the availability of talent.
React Native pros and cons
Sometimes the seeming strength of a given technology is a double-edged sword. For example, open source libraries have to be maintained by core developers and lack detailed documentation, if any. That is not the only case with React Native, so let's give it a closer look.
React Native strengths
As we just mentioned, JS is flexible in terms of applicability. Considering that it also has a relatively simple syntax, developers are attracted to it worldwide, bringing it to the top 10 of TIOBE Index.
As for the popularity of React vs Xamarin itself, the former manages to stay in higher positions, evidently. Most frameworks have seen the decline in popularity largely because of the rise of alternative technologies that are still little known at the moment.
React Native loses points to the actual native environments that are being developed by the companies behind iOS and Android. Apple works on Swift for its mobile devices, while Google tailors the Flutter framework to Android.
The loss of quality in React Native, compared to the native frameworks, is only noticeable in the case of highly complex solutions, which is shown in this particular React Native performance test. React Native imports native UI components whenever possible while other JS-based frameworks use their own components out of the box.
The case with all cross-platform development platforms is that some UI components must be given extra attention and configured separately for each different platform.
React Native WebView functionality enables developers to render web content inside their apps. It is done to display content from the web in real-time and updates dynamically. This feature is nothing unique and is present in Xamarin as well. Both frameworks are open source and are actively contributed to.
Hot reload is convenient to save the precious developer’s time and display the interface changes as soon as the code is changed, without the obligatory project rebuild.
Then there’s CodePush that automates update rollout. Any subscriber of Microsoft’s App Center can use CodePush.
React Native weaknesses
The case with every open source project is that it develops rapidly but somewhat chaotically.
React Native has a lot of libraries to choose from but it does not always mean that specific development objectives become easier to achieve.
All the readily available code will obligatorily have to be reviewed by a given React Native developer team. It might require major tweaks and, if the task is non-trivial, it is best that the team writes it from scratch.
Open source projects are also fairly hard to supply with quality documentation. Documentation could be better.
Finally, there is no perfect platform agnostic development framework. The apps built with React Native are hard to debug, and a React Native developer must either go for JS-based backend tool (like NodeJS), or know the native language of a given platform (such as C++, Java, C#...) besides JS and JSX to effectively work with backend. Otherwise, expert back end developers and testers have to take care of that.

React Native pros and cons comparison table
✅ Large talent pool available thanks to the use of JavaScript
✅ Calls to native components, which make React Native apps “look and feel” native
✅ Great performance compared to native frameworks
✅ Hot Reload feature
✅ Continuous deployment via the App Center
❌ JSX markup language raises the entry barrier
❌ Documentation fails to keep up with community contributions
❌ The native language expertise is required to effectively write and test backend code
❌ Performance drops in complex solutions
❌ JS Runtime further slows down a React Native app
React Native application examples
The best React Native apps we all know for sure are Facebook Lite and Instagram. It makes sense because Meta owns both of these products just like it spearheads the development of React Native.
What apps use React Native besides the Meta-owned ones? Skype is a curious example, considering that it is a Microsoft product.
It makes no sense to mention React Native Android apps separately from the iOS ones on the React Native apps list because, well, it is a cross-platform mobile development framework.
If we compare the popularity of Xamarin vs React Native apps, the former does not yet have a worldwide known killer app to boast.
Walmart and Bloomberg are two impressive examples. Walmart, by the way, has managed to share about 96% of the code base between iOS and Android in the course of React Native app development.
What is Xamarin?
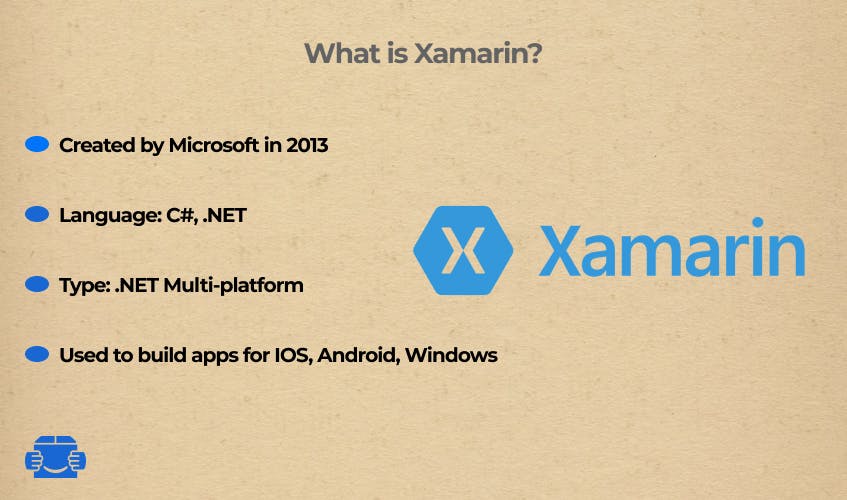
Xamarin used to be a commercial product developed by an independent studio until it was bought by Microsoft. Xamarin became open-source since then, and, as one would expect, it became more integrated with other Microsoft-backed technologies, such as C#, .NET framework, and the like.
Xamarin compiles to native assembly code both for iOS and Android, which is an advantage over technologies that use virtual machines. It would not be correct to say that Xamarin is unique in this regard. Native Development Kits (NDK) help to improve app productivity with languages you don’t regularly use for mobile developments, like C/C++ in the case of Android.
Still, React Native Android apps are expected to run slower than Xamarin apps because JS Runtime is just an extra layer between the code and the hardware.
Xamarin pros and cons
In a nutshell, Xamarin would work for a given team if they love Microsoft products and are comfortable with .NET/C# or planning integrations with other MS products, e.g., Windows Phone. Xamarin's performance is acclaimed as well.
Xamarin strengths
Xamarin user guide emphasizes high code reusability between the mainstream mobile platforms (up to 90%).
The binding mechanism ensures that functions written in C# translate to the respective functions of a given target platform: Android, iOS, or Windows Phone. It results in high, native-like performance.
As for the front end development tools, Xamarin.Forms provides exactly that: visual UI designer plus extra platform-specific tools. Developers can choose to focus on either cross-platform features and layout reusability or native design components.
Some may say that backing by Microsoft is a virtue in itself. Indeed, Xamarin blends well with Microsoft products that rely on the same technological stack.
Xamarin weaknesses
Every drawback that cross-platform mobile development frameworks suffer from applies to Xamarin as well.
It takes time to react to the updates released by iOS and Android platform developers, so Xamarin will always lag behind unless Microsoft takes over Apple or Google.
It has also been noted that Xamarin vs React Native apps tend to be larger in size, not even mentioning native apps.
The Xamarin community is smaller than that of React Native, which influences the diversity of user contributions and talent availability.
Finally, professional development comes at a price: the Visual Studio Professional has a price tag of $45 per month attached to it. Enterprise edition costs $250 monthly.

Xamarin pros and cons comparison table
✅ “Write once, run everywhere”, regarding an app’s business logic
✅ Interoperability with Java, C, C++, Objective-C
✅ Xamarin.Forms is an advanced tool for designing custom user interfaces
✅ Microsoft’s App Center provides the tools for testing apps
❌ Demonstrates the decline in popularity
❌ The UI part still has to be designed separately for each target platform
❌ Less talent available on the job market compared to React and Flutter
❌ Expensive to use in large organizations because of Visual Studio Professional or Enterprise suite prices
Xamarin application examples
It is curious that Microsoft itself does not maintain many Xamarin apps. Xamarin is involved in the MS Azure development but besides that, there is no prominent example that would ramp up the credibility of Xamarin in the eyes of newcoming users. Does Microsoft News even count?
Olo is an example of serial app development with a single code base. The business logic of all food delivery services is basically the same, so the change of the interface would look as if a brand new app had been developed. Olo developers tried this approach with JavaScript frameworks, and it failed.
In general, the more Software Architects separate business logic from UI, the more code they can reuse between platforms. Let Xamarin.Forms take care of the UI rendering differences.
Judging from the number of installs (5M+), UPS Mobile is a pretty fortunate example of Xamarin app development successes. It is a shipment tracking tool.
A great example of how to make the best of Xamarin is taking a PC app originally designed for Windows, reusing its C# code, and making a cross-platform mobile app. A Spanish MRW company did that.
Хamarin vs React Native: Comparison
Comparing Хamarin vs React Native in terms of popularity definitely reveals the latter as the winner. Developers spent approximately three times more hours on React Native development than on Xamarin, according to Statista.
There has been a race between Xamarin vs React Native vs Flutter mobile development frameworks for a while and 2022 yet has to show which one will emerge victorious. However, is their popularity well earned or merely a result of proper marketing?
No matter what, popularity implies better community support, so React Native wins this round.
As for the performance comparison, apparently, Xamarin takes the upper hand. Although JS Runtime can be fast enough depending on the use case, the general truth is that compiled languages are faster, and that ideally native languages should be used for the respective operating systems.
The UI classes between the two frameworks are basically the same, so there is no fundamental difference in, for example, how React Native Modal windows or ScrollView and the respective Xamarin objects behave. Also, consider that both frameworks have the necessary tools to work with native components.
Whether or not a given app will be able to scale and evolve is a matter of architecture. Messy architecture will surely hinder the development of any app, regardless of its framework. Still, considering that React Native apps are written in JavaScript, there is a high chance that it will be easier to port them to the web, reusing some of the code, or vice versa: port a web application to mobile. So think ahead if you want to target both web and mobile and consider picking React Native developers for that matter.
Xamarin is an open-source product but Visual Studio, which is the only IDE that works with Xamarin, is not entirely free. Large organizations have to pay a pretty penny to use VS to the full while React Native developers are free to choose any compatible environment they prefer. So again, kudos to React Native.
It is impossible to tell if a given framework will ensure faster time-to-market than the other because there are too many variables in play. It might take longer to find Xamarin developers with relevant experience considering its popularity rate and the MS Visual Studio Professional/Enterprise paywall.
Some developers argue that loose typing inherent to JavaScript introduces unnecessary risks and should be used for security-sensitive apps, such as FinTech or Health related. C#, on the other hand, is a strongly typed language. More points go off to Xamarin.
Xamarin officially supports wearables (Microsoft Band, Apple Watch, Android Wear), while React Native features open-source user-provided repositories for wearables without claiming official support.
By and large, React Native is better for most applications.
Хamarin vs React Native developers: Сosts in 2022
The salary estimates by different sources vary significantly.
According to Glassdoor, the React Native developer salary is $56-125K in the US annually, compared to $57-117K of Xamarin developers, so the difference between Хamarin vs React Native is negligible.
Talent.com, on the other hand, reports the average salary of React Native developers at $122K per year compared to $113K of Xamarin developers.
If the stats are retrieved from a large number of respondents and therefore are credible, it might indicate that either Xamarin developers are somewhat less experienced or are in lower demand – the latter being most likely.
Also, consider that nearshore or offshore outsourcing would significantly cut the salary cap. For example, if a Middle developer in Ukraine is paid $24,000 per year, their colleague from the US receives 3-5 times more for the same skill level. The average salaries in Europe tend to be a little higher while the salaries in Asia are generally even lower than that.