IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: digestible definitions, examples, and development prospects
Explore the differences between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, their characteristics, examples, benefits, and when to use one.
May 13, 2022
8 min read

At some point, these abbreviations are no more funny conundrums to you; rather, the objects of close study. Let us unveil the mystery together.
We will cover the IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS meanings one at a time.
Next up, specific IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS examples; finally, some fun facts and the development forecast for these technologies.
Cloud Computing Models Explanations
First, the definition of cloud computing would come in handy.
As opposed to on-premises servers, cloud servers are remote. Moreover, they are decentralized, which means that one cloud server does not always correspond to one piece of hardware. Cloud servers are virtual, not physical, which is why they are so easy to upscale or downscale.
A somewhat obscure way to cross-compare the types of cloud computing services with examples is by alluding to pizza:
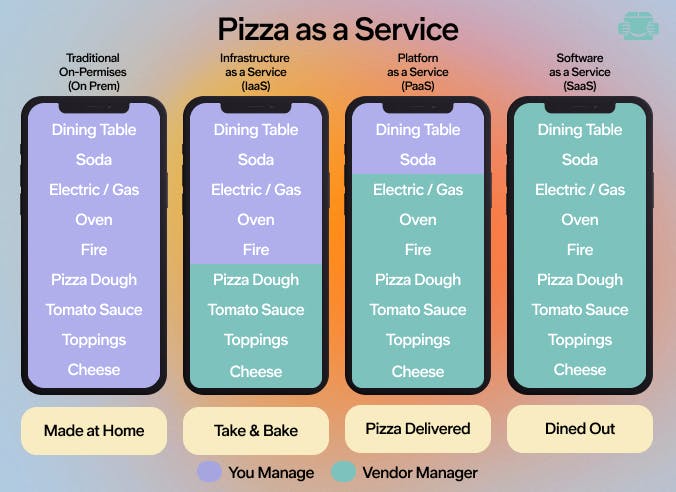
Therefore, it is easy to conclude that PaaS is an extension of IaaS, and SaaS is an extension of PaaS. Collectively, all the cloud services might be referred to as XaaS (Everything or Anything as a Service).
Cloud computing gave rise to a curious phenomena: a series of laptops that do not need installable software, relying completely on the cloud. These devices have minimum storage (about 32GB SSD or removable SD Card), a below average processor and videocard. All the software, storage, and processing power comes from a SaaS provider. This model is perfect for managing an office space with uniform devices in a safe, centralized manner.
There is also a relatively new type of cloud service: blockchain-as-a-service, which deals with cryptocurrencies, tokens, smart contracts, and advanced encryption. This technology has been gaining popularity during the last decade, creating dozens of speculative bubbles in the course of its turbulent development.
The use cases of the blockchain tech are extremely diverse. At the same time, blockchain development is a rare hard skill, and blockchain apps have their own programming language. The number of businesses that want to have this technology working out of the box keeps growing.
Serverless cloud computing takes data storage out of the equation, e.g., the service users pay only for the time their code is being executed on the cloud and the processing load.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
What is SaaS?
Salesforce defines software-as-a-service as follows: “a way of delivering applications over the Internet”. The applications in question are highly specialized, and users choose exactly which apps or “suites” they want to work with.
SaaS Characteristics
The cloud can host all kinds of applications: CRM or eHealth systems, small web or mobile apps, virtual environments, etc. The supporting infrastructure is also maintained by a SaaS provider, and a SaaS provider may turn to third-party PaaS or IaaS providers.
The apps are provided “as is” or with a range of custom alterations. Likewise, the maximum number of team and/or end users, the storage volume, artificial intelligence implementation, extended analytics, training materials and mentorship, and other special features are customizable and come at extra costs.
SaaS delivers ultimate scalability for ready-made niche solutions. As expected, SaaS solutions are highly technological and need respective skills to effectively manage. For that matter, the SaaS providers offer product trials, education, and basic software packages for minimum price.
SaaS providers also sell developer sandbox environments. In other words, SaaS providers open up access to their own custom-built platform-as-a-service products so that programming-savvy users might develop their apps.
As for the software as a service examples, it is comparable to Tetris: turn on and play. This kind of a product would not have been profitable if they were unable to scale and make profit for their creators.
Data collection and mining is one way to benefit from providing the seemingly free cloud apps. The vast quantities of data various vendors siphon from their unsuspecting users is just enough to make the right conclusions about the efficiency of their targeted ads, the right audiences, and the best marketing practices. As one would expect, these practices are not always highly ethical, so every now and then we see a giant company paying billions in penalties for manipulating users and breaching privacy.
The subscription model is another way the platforms owners like cloud apps and the users don’t. Example: An installable MS Office software package used to cost 75 bucks for a lifetime license. The modern Office 365 cloud edition costs $5 a month. It is easy to calculate how much more a prolonged use would cost compared to a one-time puchase.
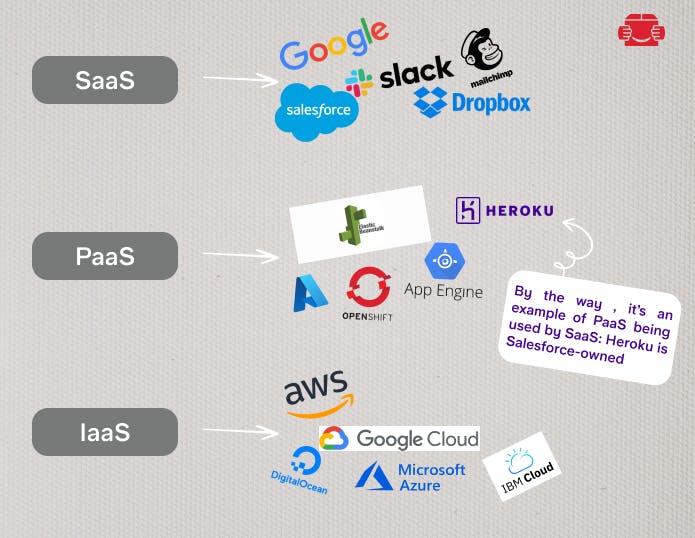
SaaS Examples
Google Suite. Office software and other cloud products for daily personal use and in business.
Salesforce. Customer relationship management (CRM) software for a variety of niches.
Slack. Corporate messenger.
Dropbox. Cross-platform cloud storage.
Mailchimp. Email marketing service.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What is PaaS?
It is more akin to software development frameworks and provides the necessary tools to develop, test, and manage apps.
PaaS Characteristics
A single developer or a team working on a cross-platform app would have to run multiple virtual OS instances to test the app, spare the time, storage, and—sometimes insufficient—computing powers to compile, build, and deploy it. Also, collect feedback. These actions sometimes involve the use of different software tools, all of which require valid licensing to work with.
PaaS provides all-in-one solutions for all of the mentioned development-related actions plus database and network management tools, and more.
Cost efficiency and simplicity are the primary features developers go for when they collaborate in PaaS environments.
PaaS provides a safe space to test applications without the need to own the infrastructure the software is being tested on.
PaaS environments work out of the box and require less time to set up than disparate development tools. They are scalable and benefit from data protection and backup measures implemented by the provider.
As a cloud service, it is synchronized between all the connected participants: the team members can work from anywhere in the world via the Internet.
Platform as a service examples boil down to large corporation-owned developer sandbox environments.
PaaS Examples
Heroku. By the way, it is an example of PaaS being used by SaaS: Heroku is Salesforce-owned.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure-as-a-service is the most basic type of cloud services: it provides storage and computing power on demand. For that reason, it is sometimes referred to as Hardware-as-a-Service.
IaaS Characteristics
IaaS has no pre-installed operating systems, frameworks, or applications, leaving it to the customer. In turn, the customer of the IaaS becomes the service provider to the end user. There are no limits (within the legal boundaries, of course) concerning the nature of the apps provided to the end users.
Third-party IaaS remove the burden of managing in-house data centers for all kinds of IT businesses, are scalable, and have flexible pricing models.
They provide solid guarantees concerning the uptime, latency, and performance. Their technical parameters are usually better than that of any in-house server. And they save your team’s effort to focus on the core activities.
Similarly, the security of physical IaaS data centers is generally higher than what an average office building has to offer.
IaaS can be used at a certain stage of application development (testing, for example) and forgone in the blink of an eye.
Thanks to competition between various IaaS providers, the users enjoy ever-improving service quality and at lowest possible market price.
IaaS Examples
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS market share
The market of niche-specific cloud software services had been rising through 2015-2020, exceeding the share of more general use case services (PaaS and IaaS). The expensiveness of SaaS solutions indicates that they are more complex.
Source: Statista.
Wrapping up
Each of the types of cloud computing services is attractive to customers (businesses and individuals) because it provides scalable, professional, low-cost solutions.
The cloud software does not need to be installed, cloud data storage is more reliable than local storage, and its computing capacity is way higher than what an ordinary PC or even SMB company server can provide.
The benefits of cloud computing are plentiful, and there is a couple of downsides, too. The use of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services entails acceptance of end user license agreements (EULA) of some kind. These agreements usually oblige users to share their data and abstain from any legal claims towards their service provider.
Cloud services require uninterrupted Internet connection.
As a rule, users are willing to sacrifice some of their liberties for the indubitable advantages of cloud services. It is possible to deploy a custom SaaS product, so you may get in touch with us and we will share some considerations concerning this possibility and the best cloud service choice in your individual case.
FAQ
What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Infrastructure-, Platform-, and Software-as-a-Service provide the following cloud services: the barebone storage and computing power, development and testing tools, and specific applications, respectively.
Which is better: IaaS or PaaS?
The applicability of cloud services depends on the goals of a particular user. “Infrastructure” in IaaS refers to hardware provision while “Platform” refers to the full suite of software development, testing, continuous delivery & continuous integration, and feedback collection tools.
What is IaaS, PaaS, SaaS with examples?
Google Docs is software (SaaS) that operates on Google Cloud (IaaS), and developers can build their own SaaS apps with Google App Engine (PaaS).
Which type of cloud computing is best?
The most expensive and complex type is Software-as-a-Service: it provides niche-specific, ready-to-use cloud applications. Platform-as-a-Service provides development tools while Infrastructure-as-a-Service provides virtual servers without specific operating systems or software out of the box.
What are the 5 main types of cloud computing?
Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, Software as a Service, Serverless, Desktop as a Service.
Which cloud service type generates the most revenue?
According to Statista, SaaS had been generating the most revenue up until 2020, without the signs of recline in the upcoming years.
What differentiates PaaS from SaaS?
The former is a cloud environment for software development whereas the latter is a library of ready-to-use software applications.